QRG: AUSTRAC Online new user sign-up
Learn when you must sign up for a user account and how to do it.
On this page
- Why you must sign up for a user account
- How to create a new user account
- How to sign up for a new user account when you accept a user invitation
Why you must sign up for a user account
You must sign up for a user account to:
- enrol a new business
- access AUSTRAC Online as a user when you accept an invitation.
If you’ve received a new user invitation email, you can use this document for instructions on how to sign up for a user account on accepting an invitation.
How to create a new user account
To create a new user account:
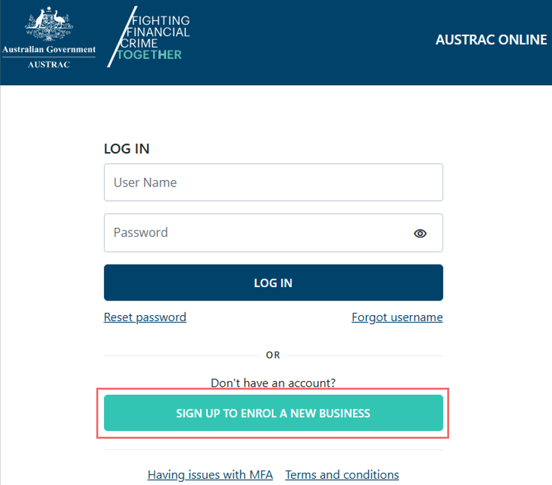
- Go to AUSTRAC Online.
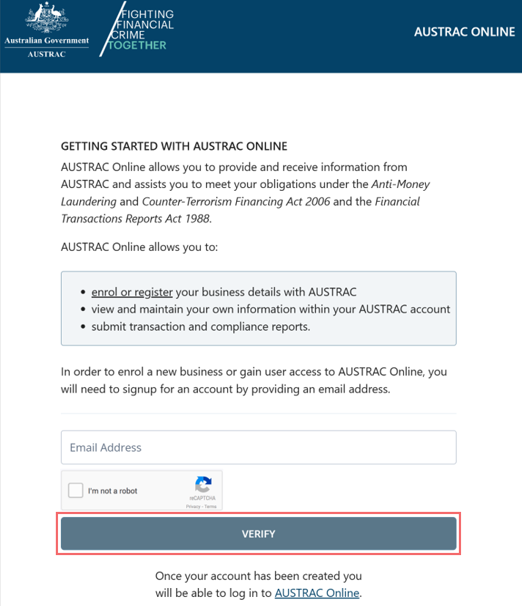
- Select Sign up to enrol a new business.
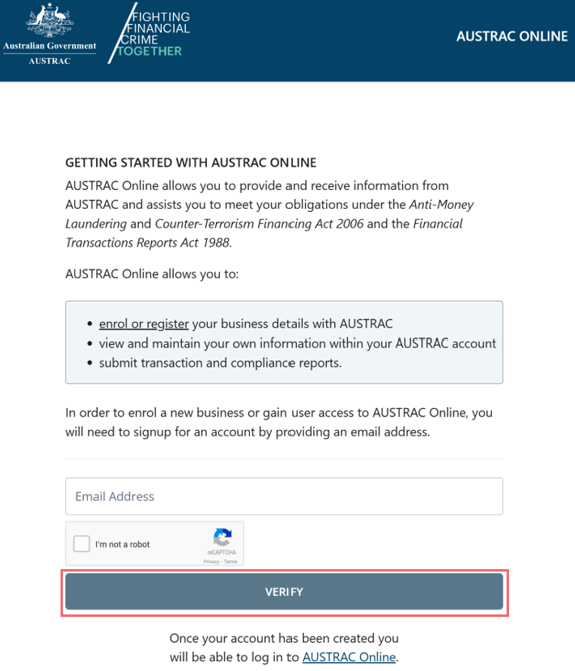
- Enter your email address.
- Complete the reCAPTCHA.
- Select Verify.
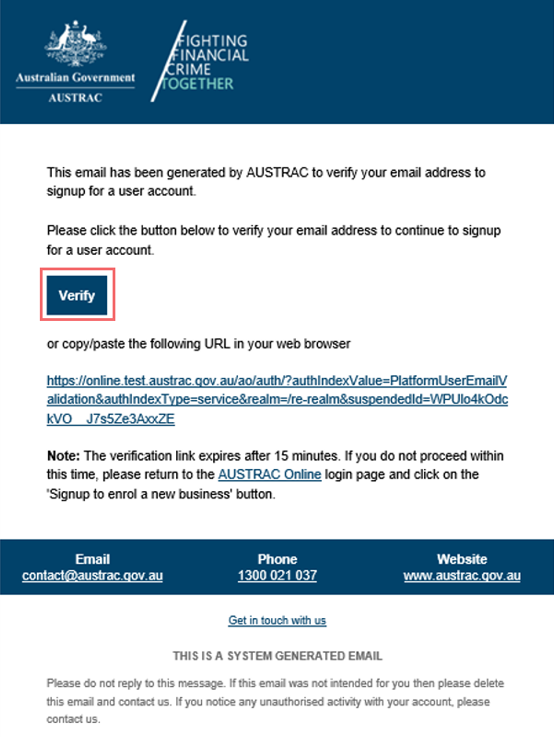
- You’ll get an email with a link to continue to sign up for a user account.
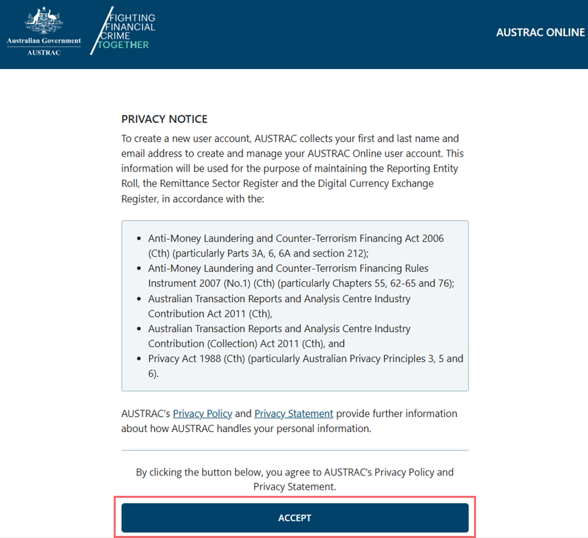
- Select Verify in the email. You’ll be directed to the privacy notice page. Read through carefully.
- Select Accept to agree to the privacy notice.
- Enter your details.
- Select Next.
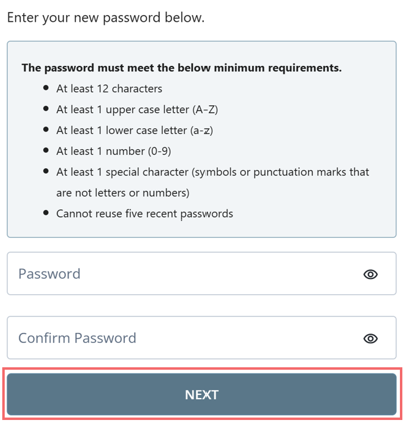
- Enter your password. Make sure it meets the listed minimum requirements.
- Select Next.
- Register for multi-factor authentication (MFA) on the next page. Go to registering for multi-factor authentication (MFA) for help.
- Once your user account has been created, you’ll get the below email to continue to enrol the new business. Go to how to enrol a business for more information on how to enrol your business.
How to sign up for a new user account when you accept a user invitation
To sign up for a user account when you accept a user invitation:
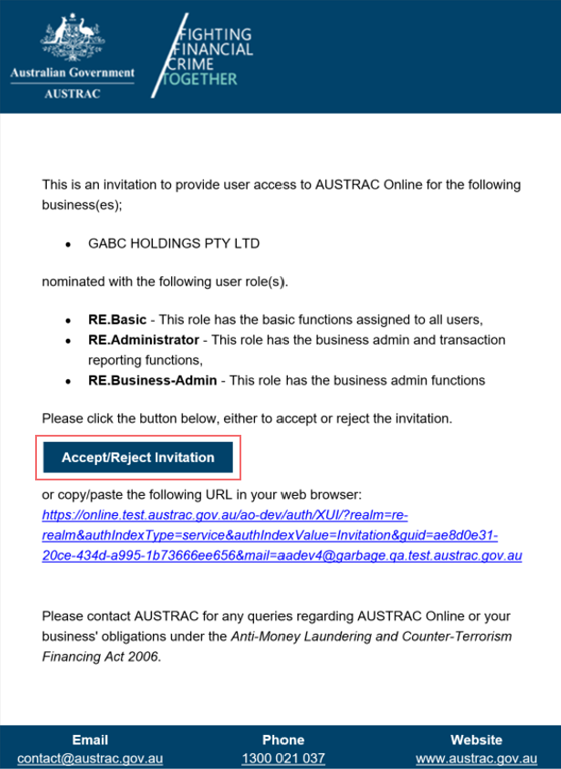
- Select the Accept/Reject invitation link in the email you got.
- Enter your email address.
- Complete the reCAPTCHA.
- Select Verify.
- When you finish signing up, you’ll have access to AUSTRAC Online.
This guidance sets out how we interpret the Act, along with associated Rules and regulations. Australian courts are ultimately responsible for interpreting these laws and determining if any provisions of these laws are contravened.
The examples and scenarios in this guidance are meant to help explain our interpretation of these laws. They’re not exhaustive or meant to cover every possible scenario.
This guidance provides general information and isn't a substitute for legal advice. This guidance avoids legal language wherever possible and it might include generalisations about the application of the law. Some provisions of the law referred to have exceptions or important qualifications. In most cases your particular circumstances must be taken into account when determining how the law applies to you.